Radar

Radar
Demo Video
In this project, we will create a radar that can detect an object within a 4 cm radius on a given angle interval using the gizDuino LIN.
WHAT IS A RADAR AND HOW DOES IT WORK?
A radar stands for radio detection and ranging. It operates on either UHF or ultra high frequency, or microwave part of the radio frequency (RF) spectrum. It is an instrument used to detect the position and movement of an object on a particular space. Its applications include tracking storm systems, forming precise maps, and detecting not just air traffic but also in aircraft and marine navigation.
Materials:
- gizDuino LIN (Arduino UNO), USB cable
- 1 x HC-SR04 sensor
- 12 x 1pin Male – Male jumper wires
- 1 x Breadboard
- 1 x Servo Motor SG-90
- 1 x Ultrasonic Sensor Holder
Download the latest version of Arduino IDE from https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software. Also, download the processing software version 2 from https://processing.org/download/The software is free and runs like the Arduino IDE.
Breadboard:
CONNECTIONS:
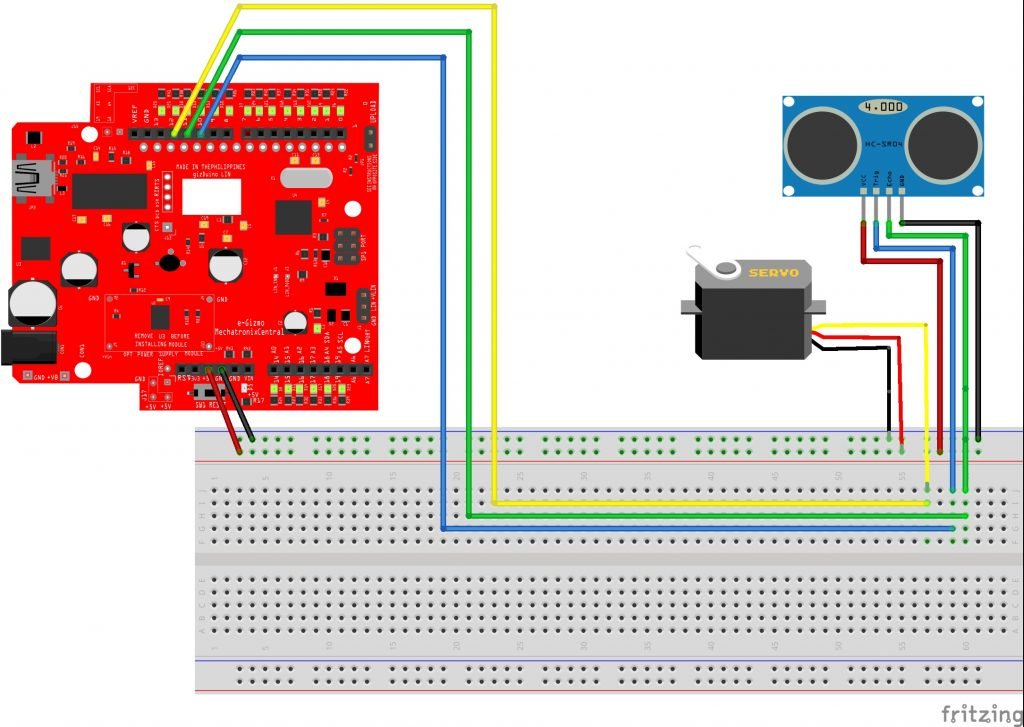
Upload the following codes to the Arduino IDE:
| // Includes the Servo library | |
| #include <Servo.h> | |
| #include <NewPing.h> | |
| int pos = 15; | |
| // Defines Tirg and Echo pins of the Ultrasonic Sensor | |
| const int trigPin = 10; | |
| const int echoPin = 11; | |
| // Variables for the duration and the distance | |
| long duration; | |
| int distance; | |
| NewPing sonar(trigPin, echoPin, 400); // NewPing setup of pins and maximum distance. | |
| Servo myServo; // Creates a servo object for controlling the servo motor | |
| void setup() { | |
| pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT); // Sets the trigPin as an Output | |
| pinMode(echoPin, INPUT); // Sets the echoPin as an Input | |
| Serial.begin(9600); | |
| myServo.attach(12); // Defines on which pin is the servo motor attached | |
| } | |
| void loop() | |
| { | |
| for ( pos = 15; pos <= 165; pos += 1) | |
| { // goes from 0 degrees to 180 degrees | |
| // in steps of 1 degree | |
| myServo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos' | |
| delay(30); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position | |
| distance = sonar.ping_cm();// Calls a function for calculating the distance measured by the Ultrasonic sensor for each degree | |
| Serial.print(pos); // Sends the current degree into the Serial Port | |
| Serial.print(","); // Sends addition character right next to the previous value needed later in the Processing IDE for indexing | |
| Serial.print(distance); // Sends the distance value into the Serial Port | |
| Serial.print("."); // Sends addition character right next to the previous value needed later in the Processing IDE for indexing | |
| } | |
| for ( pos = 165; pos >= 15; pos -= 1) | |
| { // goes from 180 degrees to 0 degrees | |
| myServo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos' | |
| delay(30); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position | |
| distance = sonar.ping_cm();// Calls a function for calculating the distance measured by the Ultrasonic sensor for each degree | |
| Serial.print(pos); // Sends the current degree into the Serial Port | |
| Serial.print(","); // Sends addition character right next to the previous value needed later in the Processing IDE for indexing | |
| Serial.print(distance); // Sends the distance value into the Serial Port | |
| Serial.print("."); // Sends addition character right next to the previous value needed later in the Processing IDE for indexing | |
| } | |
| delay(1000); | |
| } | |
| // Function for calculating the distance measured by the Ultrasonic sensor | |
| int calculateDistance(){ | |
| digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW); | |
| delayMicroseconds(2); | |
| // Sets the trigPin on HIGH state for 10 micro seconds | |
| digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH); | |
| delayMicroseconds(10); | |
| digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW); | |
| duration = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH); // Reads the echoPin, returns the sound wave travel time in microseconds | |
| distance= duration*0.034/2; | |
| return distance; | |
| } |
Upload the following codes to the Processing IDE:
| import processing.serial.*; // imports library for serial communication | |
| import java.awt.event.KeyEvent; // imports library for reading the data from the serial port | |
| import java.io.IOException; | |
| Serial myPort; // defines Object Serial | |
| // defubes variables | |
| String angle=""; | |
| String distance=""; | |
| String data=""; | |
| String noObject; | |
| float pixsDistance; | |
| int iAngle, iDistance; | |
| int index1=0; | |
| int index2=0; | |
| PFont orcFont; | |
| void setup() { | |
| size (1920, 1080); | |
| smooth(); | |
| myPort = new Serial(this,"COM4", 9600); // starts the serial communication | |
| myPort.bufferUntil('.'); // reads the data from the serial port up to the character '.'. So actually it reads this: angle,distance. | |
| orcFont = loadFont("OCRAExtended-30.vlw"); | |
| } | |
| void draw() { | |
| fill(98,245,31); | |
| textFont(orcFont); | |
| // simulating motion blur and slow fade of the moving line | |
| noStroke(); | |
| fill(0,4); | |
| rect(0, 0, width, 1010); | |
| fill(98,245,31); // green color | |
| // calls the functions for drawing the radar | |
| drawRadar(); | |
| drawLine(); | |
| drawObject(); | |
| drawText(); | |
| } | |
| void serialEvent (Serial myPort) { // starts reading data from the Serial Port | |
| // reads the data from the Serial Port up to the character '.' and puts it into the String variable "data". | |
| data = myPort.readStringUntil('.'); | |
| data = data.substring(0,data.length()-1); | |
| index1 = data.indexOf(","); // find the character ',' and puts it into the variable "index1" | |
| angle= data.substring(0, index1); // read the data from position "0" to position of the variable index1 or thats the value of the angle the Arduino Board sent into the Serial Port | |
| distance= data.substring(index1+1, data.length()); | |
| // read the data from position "index1" to the end of the data pr thats the value of the distance | |
| // converts the String variables into Integer | |
| iAngle = int(angle); | |
| iDistance = int(distance); | |
| } | |
| void drawRadar() { | |
| pushMatrix(); | |
| translate(960,1000); // moves the starting coordinats to new location | |
| noFill(); | |
| strokeWeight(2); | |
| stroke(98,245,31); | |
| // draws the arc lines | |
| arc(0,0,1800,1800,PI,TWO_PI); | |
| arc(0,0,1400,1400,PI,TWO_PI); | |
| arc(0,0,1000,1000,PI,TWO_PI); | |
| arc(0,0,600,600,PI,TWO_PI); | |
| // draws the angle lines | |
| line(-960,0,960,0); | |
| line(0,0,-960*cos(radians(30)),-960*sin(radians(30))); | |
| line(0,0,-960*cos(radians(60)),-960*sin(radians(60))); | |
| line(0,0,-960*cos(radians(90)),-960*sin(radians(90))); | |
| line(0,0,-960*cos(radians(120)),-960*sin(radians(120))); | |
| line(0,0,-960*cos(radians(150)),-960*sin(radians(150))); | |
| line(-960*cos(radians(30)),0,960,0); | |
| popMatrix(); | |
| } | |
| void drawObject() { | |
| pushMatrix(); | |
| translate(960,1000); // moves the starting coordinats to new location | |
| strokeWeight(9); | |
| stroke(255,10,10); // red color | |
| pixsDistance = iDistance*22.5; // covers the distance from the sensor from cm to pixels | |
| // limiting the range to 40 cms | |
| if(iDistance<40){ | |
| // draws the object according to the angle and the distance | |
| line(pixsDistance*cos(radians(iAngle)),-pixsDistance*sin(radians(iAngle)),950*cos(radians(iAngle)),-950*sin(radians(iAngle))); | |
| } | |
| popMatrix(); | |
| } | |
Version of the codes that will fit into any resolution of the screen:
| /*Radar Project | |
| * | |
| * Updated version. Fits any screen resolution! | |
| * Just change the values in the size() function, | |
| * with your screen resolution. | |
| * | |
| * by Dejan Nedelkovski, | |
| * www.HowToMechatronics.com | |
| * | |
| */ | |
| import processing.serial.*; // imports library for serial communication | |
| import java.awt.event.KeyEvent; // imports library for reading the data from the serial port | |
| import java.io.IOException; | |
| Serial myPort; // defines Object Serial | |
| // defubes variables | |
| String angle=""; | |
| String distance=""; | |
| String data=""; | |
| String noObject; | |
| float pixsDistance; | |
| int iAngle, iDistance; | |
| int index1=0; | |
| int index2=0; | |
| PFont orcFont; | |
| void setup() { | |
| size (1920, 1080); // ***CHANGE THIS TO YOUR SCREEN RESOLUTION*** | |
| smooth(); | |
| myPort = new Serial(this,"COM4", 9600); // starts the serial communication | |
| myPort.bufferUntil('.'); // reads the data from the serial port up to the character '.'. So actually it reads this: angle,distance. | |
| orcFont = loadFont("OCRAExtended-30.vlw"); | |
| } | |
| void draw() { | |
| fill(98,245,31); | |
| textFont(orcFont); | |
| // simulating motion blur and slow fade of the moving line | |
| noStroke(); | |
| fill(0,4); | |
| rect(0, 0, width, height-height*0.065); | |
| fill(98,245,31); // green color | |
| // calls the functions for drawing the radar | |
| drawRadar(); | |
| drawLine(); | |
| drawObject(); | |
| drawText(); | |
| } | |
| void serialEvent (Serial myPort) { // starts reading data from the Serial Port | |
| // reads the data from the Serial Port up to the character '.' and puts it into the String variable "data". | |
| data = myPort.readStringUntil('.'); | |
| data = data.substring(0,data.length()-1); | |
| index1 = data.indexOf(","); // find the character ',' and puts it into the variable "index1" | |
| angle= data.substring(0, index1); // read the data from position "0" to position of the variable index1 or thats the value of the angle the Arduino Board sent into the Serial Port | |
| distance= data.substring(index1+1, data.length()); // read the data from position "index1" to the end of the data pr thats the value of the distance | |
| // converts the String variables into Integer | |
| iAngle = int(angle); | |
| iDistance = int(distance); | |
| } | |
| void drawRadar() { | |
| pushMatrix(); | |
| translate(width/2,height-height*0.074); // moves the starting coordinats to new location | |
| noFill(); | |
| strokeWeight(2); | |
| stroke(98,245,31); | |
| // draws the arc lines | |
| arc(0,0,(width-width*0.0625),(width-width*0.0625),PI,TWO_PI); | |
| arc(0,0,(width-width*0.27),(width-width*0.27),PI,TWO_PI); | |
| arc(0,0,(width-width*0.479),(width-width*0.479),PI,TWO_PI); | |
| arc(0,0,(width-width*0.687),(width-width*0.687),PI,TWO_PI); | |
| // draws the angle lines | |
| line(-width/2,0,width/2,0); | |
| line(0,0,(-width/2)*cos(radians(30)),(-width/2)*sin(radians(30))); | |
| line(0,0,(-width/2)*cos(radians(60)),(-width/2)*sin(radians(60))); | |
| line(0,0,(-width/2)*cos(radians(90)),(-width/2)*sin(radians(90))); | |
| line(0,0,(-width/2)*cos(radians(120)),(-width/2)*sin(radians(120))); | |
| line(0,0,(-width/2)*cos(radians(150)),(-width/2)*sin(radians(150))); | |
| line((-width/2)*cos(radians(30)),0,width/2,0); | |
| popMatrix(); | |
| } | |
| void drawObject() { | |
| pushMatrix(); | |
| translate(width/2,height-height*0.074); // moves the starting coordinats to new location | |
| strokeWeight(9); | |
| stroke(255,10,10); // red color | |
| pixsDistance = iDistance*((height-height*0.1666)*0.025); // covers the distance from the sensor from cm to pixels | |
| // limiting the range to 40 cms | |
| if(iDistance<40){ | |
| // draws the object according to the angle and the distance | |
| line(pixsDistance*cos(radians(iAngle)),-pixsDistance*sin(radians(iAngle)),(width-width*0.505)*cos(radians(iAngle)),-(width-width*0.505)*sin(radians(iAngle))); | |
| } | |
| popMatrix(); | |
| } | |
| void drawLine() { | |
| pushMatrix(); | |
| strokeWeight(9); | |
| stroke(30,250,60); | |
| translate(width/2,height-height*0.074); // moves the starting coordinats to new location | |
| line(0,0,(height-height*0.12)*cos(radians(iAngle)),-(height-height*0.12)*sin(radians(iAngle))); // drawsthe line according to the angle | |
| popMatrix(); | |
| } | |
| void drawText() { // draws the texts on the screen | |
| pushMatrix(); | |
| if(iDistance>40) { | |
| noObject = "Out of Range"; | |
| } | |
| else { | |
| noObject = "In Range"; | |
| } | |
| fill(0,0,0); | |
| noStroke(); | |
| rect(0, height-height*0.0648, width, height); | |
| fill(98,245,31); | |
| textSize(25); | |
| text("10cm",width-width*0.3854,height-height*0.0833); | |
| text("20cm",width-width*0.281,height-height*0.0833); | |
| text("30cm",width-width*0.177,height-height*0.0833); | |
| text("40cm",width-width*0.0729,height-height*0.0833); | |
| textSize(40); | |
| text("Object: " + noObject, width-width*0.875, height-height*0.0277); | |
| text("Angle: " + iAngle +" °", width-width*0.48, height-height*0.0277); | |
| text("Distance: ", width-width*0.26, height-height*0.0277); | |
| if(iDistance<40) { | |
| text(" " + iDistance +" cm", width-width*0.225, height-height*0.0277); | |
| } | |
| textSize(25); | |
| fill(98,245,60); | |
| translate((width-width*0.4994)+width/2*cos(radians(30)),(height-height*0.0907)-width/2*sin(radians(30))); | |
| rotate(-radians(-60)); | |
| text("30°",0,0); | |
| resetMatrix(); | |
| translate((width-width*0.503)+width/2*cos(radians(60)),(height-height*0.0888)-width/2*sin(radians(60))); | |
| rotate(-radians(-30)); | |
| text("60°",0,0); | |
| resetMatrix(); | |
| translate((width-width*0.507)+width/2*cos(radians(90)),(height-height*0.0833)-width/2*sin(radians(90))); | |
| rotate(radians(0)); | |
| text("90°",0,0); | |
| resetMatrix(); | |
| translate(width-width*0.513+width/2*cos(radians(120)),(height-height*0.07129)-width/2*sin(radians(120))); | |
| rotate(radians(-30)); | |
| text("120°",0,0); | |
| resetMatrix(); | |
| translate((width-width*0.5104)+width/2*cos(radians(150)),(height-height*0.0574)-width/2*sin(radians(150))); | |
| rotate(radians(-60)); | |
| text("150°",0,0); | |
| popMatrix(); | |
| } | |
Documented by: Joel Jambalos
For more details about the projects, see the following reference:
For Radar:
Nedelkovski, D. (n.d.). Arduino Radar Project. Retrieved from https://howtomechatronics.com/projects/arduino-radar-project/Rouse, M. (n.d.).
Definition of Radar. Retrieved August 6, 2018, from https://searchmobilecomputing.techtarget.com/definition/radar



















 by
by
Leave a Comment